Manual Testing Tutorial: What it is, how to do it, and tools used with examples
A complete manual testing tutorial covering all aspects of manual testing, including techniques, types, and best practices.
Manual testing in software development refers to manually creating and executing test cases without using automation tools. This approach aims to uncover software application issues, bugs, and defects, ensuring its quality and functionality. It's worth noting that manual testing is not only the most commonly used method but also a cost-effective way to evaluate the functionality and performance of a software application.
When it comes to performing tests, there are two primary methods used by Quality Assurance (QA) professionals. The first involves manually executing test cases as outlined in the written test plan, going through each step to identify potential issues. The second method involves automating test scenarios using test automation frameworks, which helps streamline the testing process.
Even though automated testing plays a crucial role in revolutionizing testing practices, the significance of manual testing cannot be ignored. For example, retesting bug fixes and patches in the staging environment before production release, providing automation test reports to manual QA teams for identifying failures, delivering product knowledge transfer to new automation engineers, and addressing low-priority bugs in the backlog. However, there can also be more aspects where manual intervention is required.
What is Manual Testing?
Manual testing involves a QA engineer testing a software application manually to find bugs. They follow a written test plan with specific test scenarios and analyze the website or app's performance from a user's point of view. QAs check if the software behaves as expected, and any differences are noted as bugs.
It's particularly important in exploratory testing or cases executed a few times, helping QAs find bugs early in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
This approach is suitable for testing smaller software projects. Manual testing is still necessary in larger projects with thousands or millions of test cases, to see if it's feasible to automate certain test cases.
Manual testing is important because it helps developers understand how their application behaves, its usability, and overall user experience. It's also helpful in finding issues that might be missed in automated tests.
In the next section, we will understand the importance of manually testing the software applications.
Why is Manual Testing Important?
Every day, loads of new software applications hit the market. To make sure these software applications work flawlessly, it's crucial to use both manual testing along with automated testing. Here are four reasons why manual testing is super important:
- Humans play a significant role in checking how easy and user-friendly an app is. Automation tools are improving, but they can't beat human intuition. Humans are creative when performing testing and can test software in ways that automated testing might miss. So, if a software application is built for people, it makes sense for a human to test it before releasing it to everyone.
- Test scripts are efficient but can run into unexpected issues, causing nightmares for developers. False positives are part of automation, leading to inaccurate test results. Human input adds an extra layer of digital confidence and ensures the app is reliable.
- Automated testing is suitable for certain tasks, but they can't go beyond their set scenarios. That's where manual exploratory testing comes in. Skilled human testers use their creativity and experience to perform quality testing in a systematic manner. This method often uncovers bugs at least expected places.
- Agile development works alongside testing, and test automation is crucial for efficiency. But manual testing is fast and helps with cases that aren't automated. In busy development cycles, there might not be time to automate everything, so manual testing is a smart move. Also, there's no need to spend time automating tests done only once, like edge cases.
- There are situations where test automation isn't the best fit or isn't feasible. This might be because of certain limitations in the technologies itself, dealing with highly complex processes that are challenging to automate effectively, or when considering the balance between the efforts invested and the expected return on investment (ROI). In such cases, relying on manual processes remains a feasible approach to ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of the testing process.
Manual testing is a hands-on, time-consuming process with the potential for human errors, yet it offers the freedom to explore and doesn't require technical programming skills or predefined frameworks. However, its reliance on human judgment can lead to slightly less accurate results compared to automated methods. Let’s look at the characteristics of the manual test process in the next section.
Characteristics of Manual Testing
Shown below are the characteristics of the manual testing process:
- Manual testing takes a considerable amount of time as human testers go through the software step by step. Unlike automated testing, where automation tools can do things quickly, manual testing needs the careful attention of a tester, making it a bit slow.
- Since humans are doing the testing, there's a greater chance of human errors. Testers might overlook some aspects or make specific errors. This is why manual testing isn't as foolproof as automated testing when it comes to avoiding errors.
- In manual testing, testers can explore the software in different ways to check the software’s behavior. This allows them to discover issues that might not be identified during automation.
- Unlike automated testing, manual testing doesn't require testers to know any programming languages. Testers use the software like regular users, checking if everything works as it should without needing to write complex code.
- In manual testing, testers don't rely on automation frameworks or tools. They interact directly with the software, using their judgment and processes rather than following a framework guidelines.
- Manual testing may not be as precise as automated testing. Since it depends on human skills, there's room for interpretation, and results may vary between testers. This means it might miss every minor issue that automated testing could detect.
Advantages and Shortcomings of Manual Testing
Manual testing is helpful, particularly for its flexibility, human insight, and cost-effectiveness in specific situations. However, its limitations in speed, scalability, and consistency highlight the need for a balanced approach, often combined with automated testing for a comprehensive quality assurance strategy. Let’s discuss the pros and cons of manual testing.
- Human Intelligence: Testers can leverage their creativity to think outside the box, uncovering bugs that might escape during automated testing. They can explore scenarios beyond pre-defined test cases and detect usability issues.
- Flexibility: Manual testing adapts to dynamic interfaces and changing requirements. It's perfect for testing early prototypes or features under development.
- Usability and Accessibility: Testers can effectively evaluate user experience, interface intuitiveness, and accessibility compliance. They can provide valuable insights on how real users might interact with the software.
- Cost-effectiveness: For small software projects with limited budgets, manual testing can be cheaper than setting up and maintaining automation frameworks.
Shortcomings:
- Subjectivity: Results can be subjective and prone to human error. Different testers might reach different conclusions about the same test case.
- Time-Consuming: Manually testing large and complex software applications can be tedious, especially for repetitive tasks. This can delay deadlines and increase project costs.
- Inconsistency: Manual testing might not be consistent across multiple test runs, making it challenging to track regressions and ensure reliable results.
- Limited Scope: Testers can only explore a limited number of scenarios compared to automated scripts that can run hundreds or thousands of tests simultaneously.
- Reliance on Tester expertise: The quality of testing heavily depends on the skill and experience of the tester which can introduce potential bottlenecks.
Choosing between manual and automation testing can depend on your project requirements, budget constraints, and the nature of the software being developed. However, you can use a blended or hybrid approach to leverage the advantages of both methods. To have a better clarity of this, let’s understand how manual testing is different from automation testing.
Manual Testing vs Automation Testing
| Feature | Manual Testing | Automation Testing |
|---|
| Execution | Test cases are executed manually by human testers. | Test cases are executed using automated tools or frameworks. |
| Speed and efficiency | Typically slower and less efficient. | Faster and more efficient, especially for repetitive tasks. |
| Human Involvement | Relies on human testers for test execution and analysis. | Involves minimal human intervention once test scripts are created. |
| Adaptability | Flexible and adaptable to changes. | Less adaptable to frequent changes in requirements. |
| Exploratory Testing | Ideal for exploratory testing. | Less effective for exploratory testing as it follows predefined test scripts. |
| Cost | More cost-effective for small-scale projects. | Initial setup and tool costs may be high but cost-effective in the long run for repetitive testing. |
| Test Coverage | Depends on the tester's expertise. | Can provide comprehensive coverage, especially for extensive scenarios. |
| Regression Testing | Prone to human error in repetitive scenarios. | Well-suited for regression testing, ensuring stability after changes. |
| Skill Requirement | Manual testing skills, and domain knowledge are required. | Requires programming and scripting skills and testing expertise. |
| Early Detection of Defects | Defects may be identified later in the lifecycle | Enables early defect detection, especially in continuous integration pipelines. |
To perform manual testing, different methods or techniques are used, each customized to address specific facets of software testing. Let’s discuss the techniques of manual testing in the next section.
Core Manual Testing Techniques
Manual testing comes in various forms, each designed for specific purposes and types of software. Here, we'll look at some of the common types:
- Black Box Testing: It is a method where the internal workings of a software application are ignored, and the emphasis is placed on evaluating the system's external behavior. Testers interact with the software through inputs and examine the outputs to ensure they align with expected results. This approach allows for a comprehensive testing in terms of functionality, performance, and user experience without requiring knowledge of the internal code structure. It is particularly valuable for validating that the software meets specified requirements and behaves as intended from the user's perspective.
- White Box Testing: In contrast to black-box testing, white-box testing is a method that delves into the internal structure of a software application. Testers validate the code, logic, and architecture to check the security, functionality, and overall quality of the software. Typically performed by developers or quality assurance professionals with a deep understanding of the internal workings, white box testing aims to identify issues such as coding errors, and security vulnerabilities. It provides a more detailed testing of the software's internal components, ensuring a thorough evaluation of its reliability and adherence to coding standards.
- Grey Box Testing: It is a testing technique that combines aspects of both black-box and white-box testing. It emphasizes the testing of some internal components while not delving into all aspects. The tester has partial knowledge of the system's internal details. Grey box testing is often used in system integration testing, where assessing the interaction of various components is crucial for detailed testing.
Now you know the different techniques of manual testing, let’s look at the types of testing software applications manually.
Types of Manual Testing
Manual testing comprises various stages, such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, user interface (UI) testing, and acceptance testing. However, these stages may not follow a sequential order. Depending on your software project requirements, there can be overlap or a different sequence of these stages.
- Unit Testing: It is a testing approach where individual units or components of a software application are isolated and tested independently. The objective is to verify that each unit functions as intended, ensuring that the minor testable parts of the code meet specified requirements. Typically conducted by developers during the development phase, unit testing helps identify errors early in the process, promoting code reliability and maintainability. It is an integral part of the Software Development Life Cycle, contributing to the development of robust and modular code.
- System Testing: It provides a comprehensive evaluation of the entire software system to ensure that all integrated components function as a complete entity. It follows unit and integration testing and checks the system's compliance with specified requirements. This testing phase involves testing the software in a holistic manner, validating its performance, security, and overall functionality. System testing aims to identify issues that may arise from the interaction of integrated components, providing a thorough validation of the software's capabilities before it is released to end-users.
- Integration Testing: This testing phase focuses on checking the interaction between different components or modules of a software application. Integration testing ensures that the various components of the software work together seamlessly, ensuring that data is exchanged correctly and that the integrated system functions as expected. It helps detect interface defects, communication issues, and inconsistencies that may arise during the integration process, contributing to the overall reliability of the software.
- UI Testing: It checks the look and feel of the software's user interface, covering things like layout, design, responsiveness, and how easy it is to use. UI testing also ensures the user interface stays consistent whether you're using it on different devices or web browsers.
- Acceptance Testing: It is the final phase in the testing process before software is deployed. This testing is conducted to validate that the software meets the specified requirements and is acceptable for delivery to end-users. Typically performed by end-users or stakeholders, acceptance testing aims to ensure that the software fulfills its intended purpose and aligns with user expectations. This phase includes confirming that all features work as intended, addressing any outstanding issues, and obtaining final approval for the software release. Acceptance testing provides a crucial validation step to ensure that the software is ready for deployment and meets the needs of its intended users.
No matter how testers decide to perform manual testing, they all need to stick to the Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC). The primary difference comes down to how they carry out the testing. In the next section, let’s explore the manual testing process.
Manual Testing Process
The manual test process takes time, but it's the human touch that makes this kind of testing really effective in achieving a high-quality software product. Manual testing is simple compared to automation testing since it requires fewer technical skills, and you don't have to deal with learning or setting up automation testing tools.
However, testers still need to be familiar with various manual testing methods. Like any software testing, the main goal of manual testing is to check the system against the specified requirements or user stories, find bugs, and help the development team create software applications without defects.
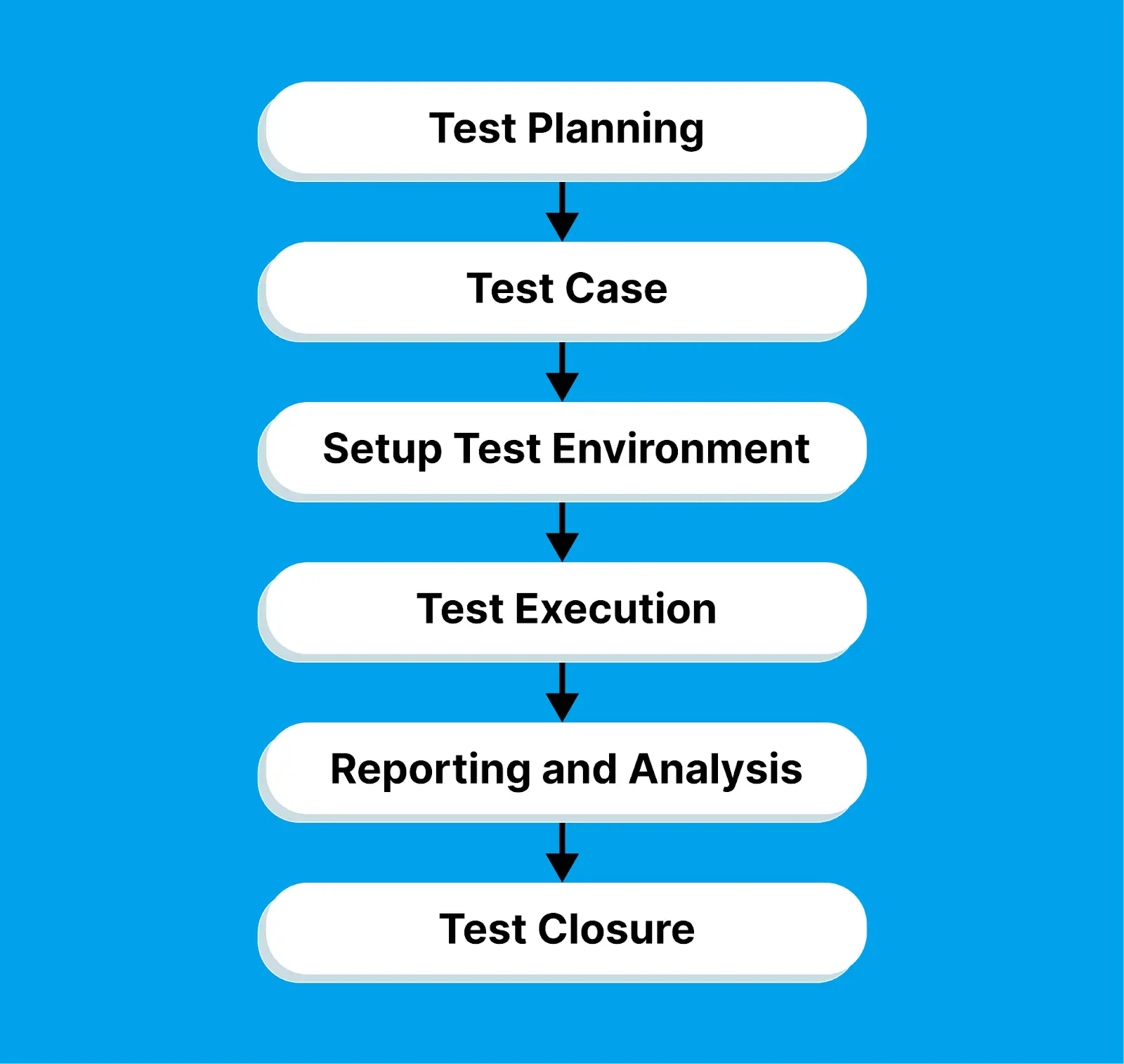
Here are the steps involved in the manual testing process:
- Test Planning: The starting point in manual testing is test planning. Testers get familiar with user requirements and design documents, figuring out how to identify test goals, define the testing strategy, and create a comprehensive test plan. This plan lays out the testing approach, along with necessary resources and timelines.
- Test Case: Next up is creating the test cases. The manual test case development involves detailing the steps to follow, the expected results, and any prerequisites or test data requirements.
- Setup Test environment: Following test case design, it's time to set up the test environment. This includes configuring hardware, software, and network settings necessary for the tests. It also involves installing applications, databases, web servers, or any other components needed for running the tests.
- Test execution: With all the planning and setup done, testers then execute the test cases. They interact with the software application's user interface, checking if its behavior aligns with the expected outcomes outlined in the user specification documents.
- Reporting and Analysis: Any defects or issues discovered during testing are documented and reported to the relevant teams for resolution. Reports include screenshots, testing conditions, and details of the faults. Developers analyze the assigned issues and determine the best approach for resolving them as quickly as possible.
- Test Closure: In the final stage, testers review the test execution results, assessing if the testing objectives have been achieved. They re-evaluate defects fixed by developers and close the issues if the faults are resolved. Test summary reports are generated, highlighting test coverage, the number of defects found, and other relevant metrics for stakeholders. In some cases, test closure may also involve documenting best practices and preparing for future testing cycles.
In the upcoming section, we will understand the above manual test process with the help of an example.
Example of Manual Testing
Consider a scenario involving manual testing for an eCommerce website. This real-life example demonstrates how manual testing is essential to ensure a seamless and user-friendly experience on an eCommerce website, covering critical processes like user registration and the checkout journey.
Test Scenario: User Registration and Checkout Process
Test Planning
- Ensure smooth user registration and checkout process.
- Manually validate each step of the registration and checkout process to identify any issues that might hinder a user from successfully registering and completing a purchase.
- Outline specific test cases, including scenarios for successful registration, failed registration, and various checkout scenarios.
Test Case Designing
- Test Case 1: Successful Registration Steps: Navigate to the registration page, fill in valid user details, and submit the form. Expected Result: User receives a confirmation message and can log in.
- Test Case 2: Failed Registration Steps: Attempt registration with invalid or incomplete information. Expected Result: Appropriate error messages are displayed.
- Test Case 3: Checkout Process Steps: Add items to the cart, proceed to checkout, and complete the purchase. Expected Result: Successful order placement, confirmation email received.
Test environment Setup
- Set up the test environment for testing, including hardware, software, networking configuration, and more.
Test execution
- Execute each test case.
- Interact with the website's user interface to ensure the expected outcomes are met.
Reporting and Analysis
- Document any issues encountered during the registration and checkout process.
- Include screenshots, error messages, and detailed descriptions of the issues.
Defect Fix & Re-Verification
- Developers address reported issues.
- Testers re-verify the fixed issues to ensure they are resolved.
Test Closure
- Review overall test results and confirm that the user registration and checkout processes meet the defined objectives.
- Generate a test summary report with insights into the testing coverage and any outstanding issues.
When it comes to testing software applications manually, you get two options: test on the local machine or the cloud. Most organizations prefer to test on a cloud as it offers scalability and reliability and eliminates the hassle of setting up an in-house infrastructure. This helps testers validate their websites and mobile applications across different real browsers, devices, and operating systems.
AI-powered test orchestration and execution platforms like LambdaTest let you perform manual web and mobile app testing on an online grid of different browsers, devices, and operating systems combinations. In the next section, let’s see how to perform manual testing on a cloud-based platform like LambdaTest.
Note : Run your manual test cases across 3000+ desktop and mobile browsers. Try LambdaTest Now!
How to Perform Manual Testing on the Cloud?
Cloud testing platforms like LambdaTest let you manually test websites on real operating systems (Windows and macOS) and mobile apps on virtual and real device cloud (Android and iOS).
Manual Browser Testing
LambdaTest also lets you perform manual web testing on desktop and mobile environments. For demonstration, let’s look at how to test websites manually on the desktop using the LambdaTest cloud.
- Login to your LambdaTest account. If you don’t have an account, register on LambdaTest.
- Go to Real Time > Browser Testing.
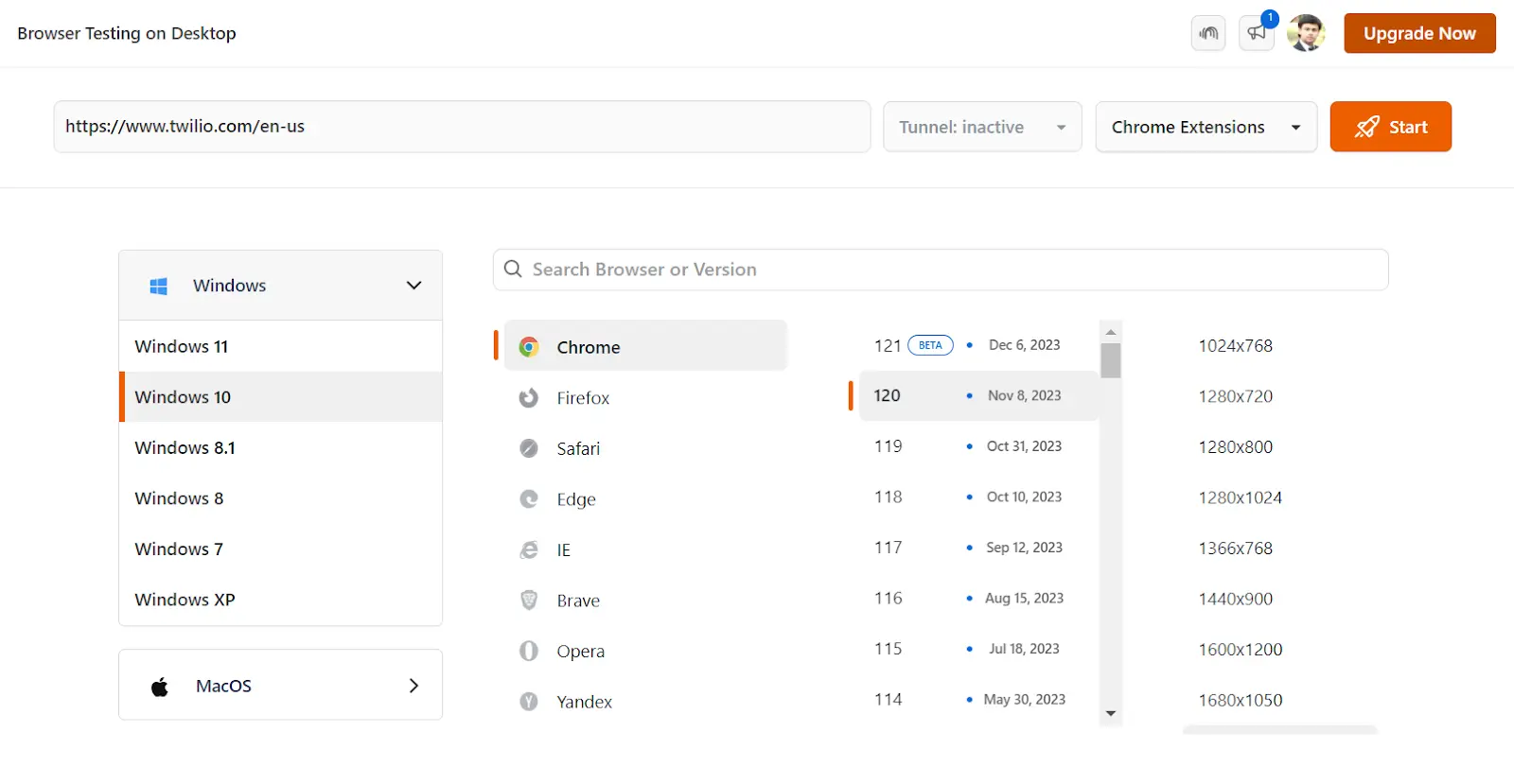
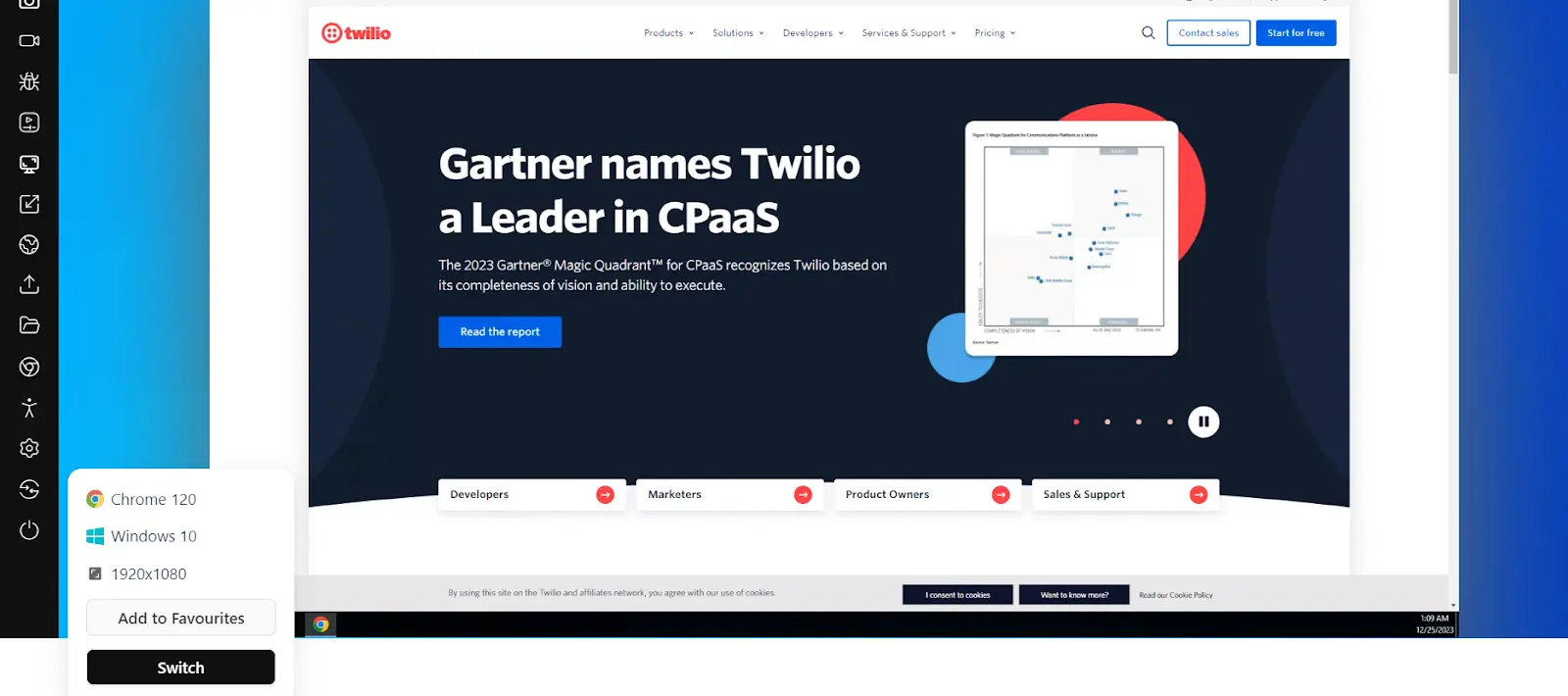
- Enter a test URL, select the browser, and choose VERSION, OS, and RESOLUTION. Then, click START.
 A cloud-based operating system will be launched where you can manually test your websites and web applications.
A cloud-based operating system will be launched where you can manually test your websites and web applications.
Manual App Testing
In this section, let’s look at how to test mobile apps manually on the LambdaTest cloud.
- To test on Android emulators or iOS simulators, select Real Time > App Testing from the left sidebar. To test on real devices, choose Real Device > App Testing.
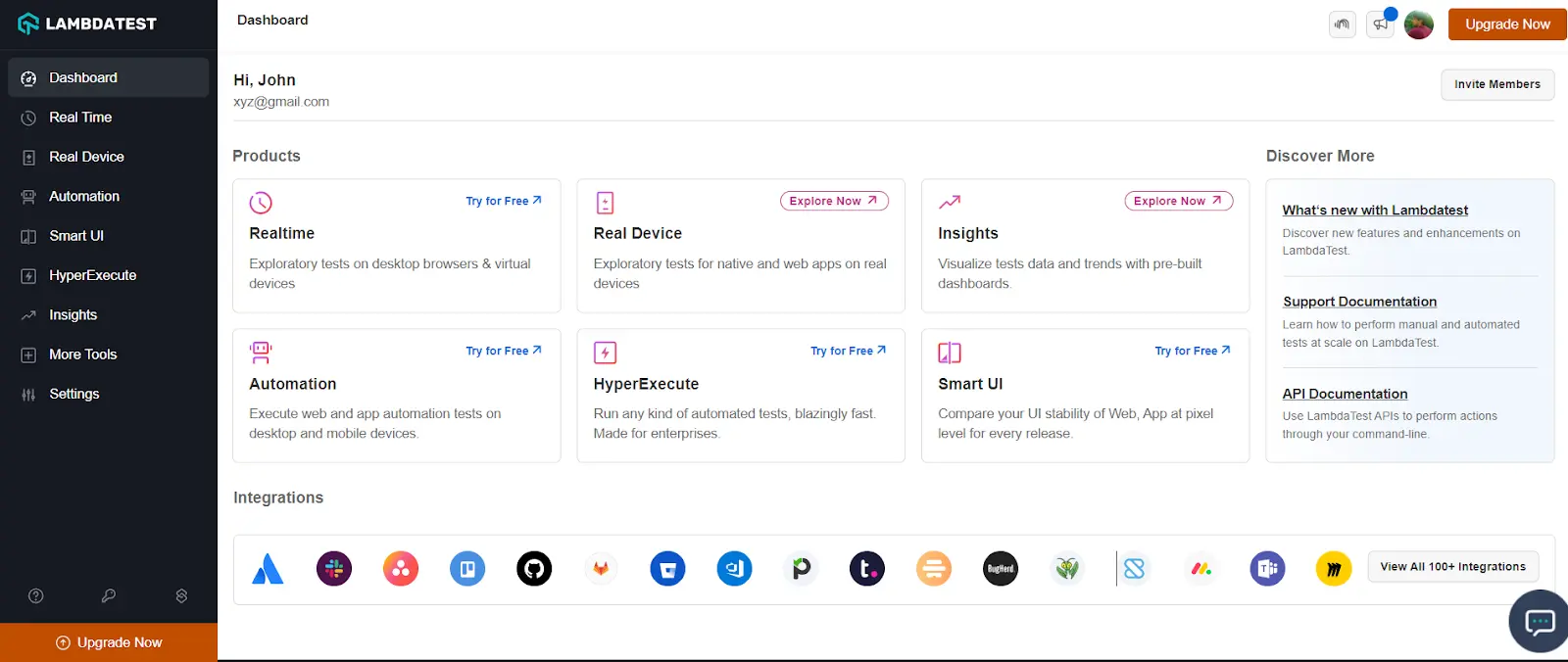 For demonstration purposes, let’s choose Real Device.
For demonstration purposes, let’s choose Real Device.
- Choose the mobile platform (Android/iOS), and upload your app. For instance, if you want to test on iPhone, select the iPhone or iPad and choose the model on which you wish to trigger the tests. Then, click Start.
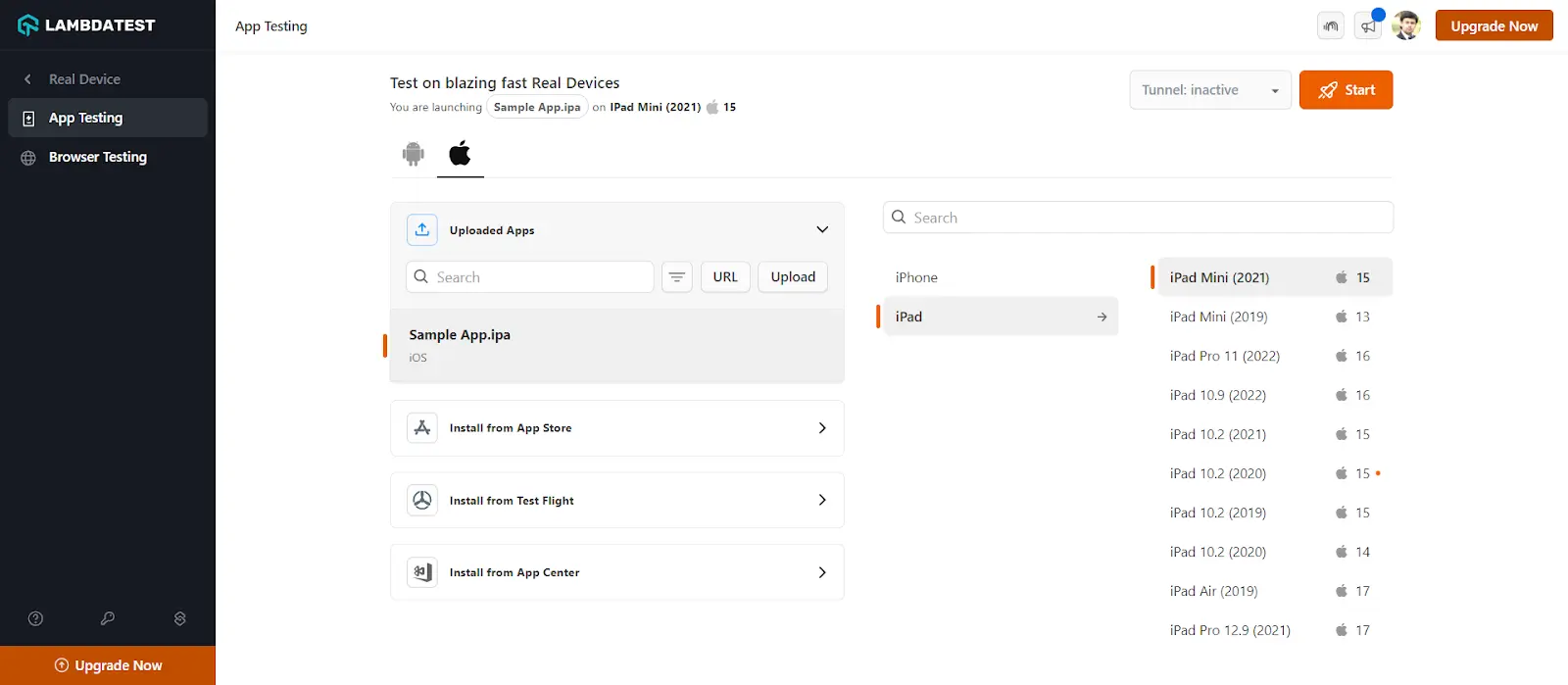 It will route you to the selected cloud-based device.
It will route you to the selected cloud-based device. 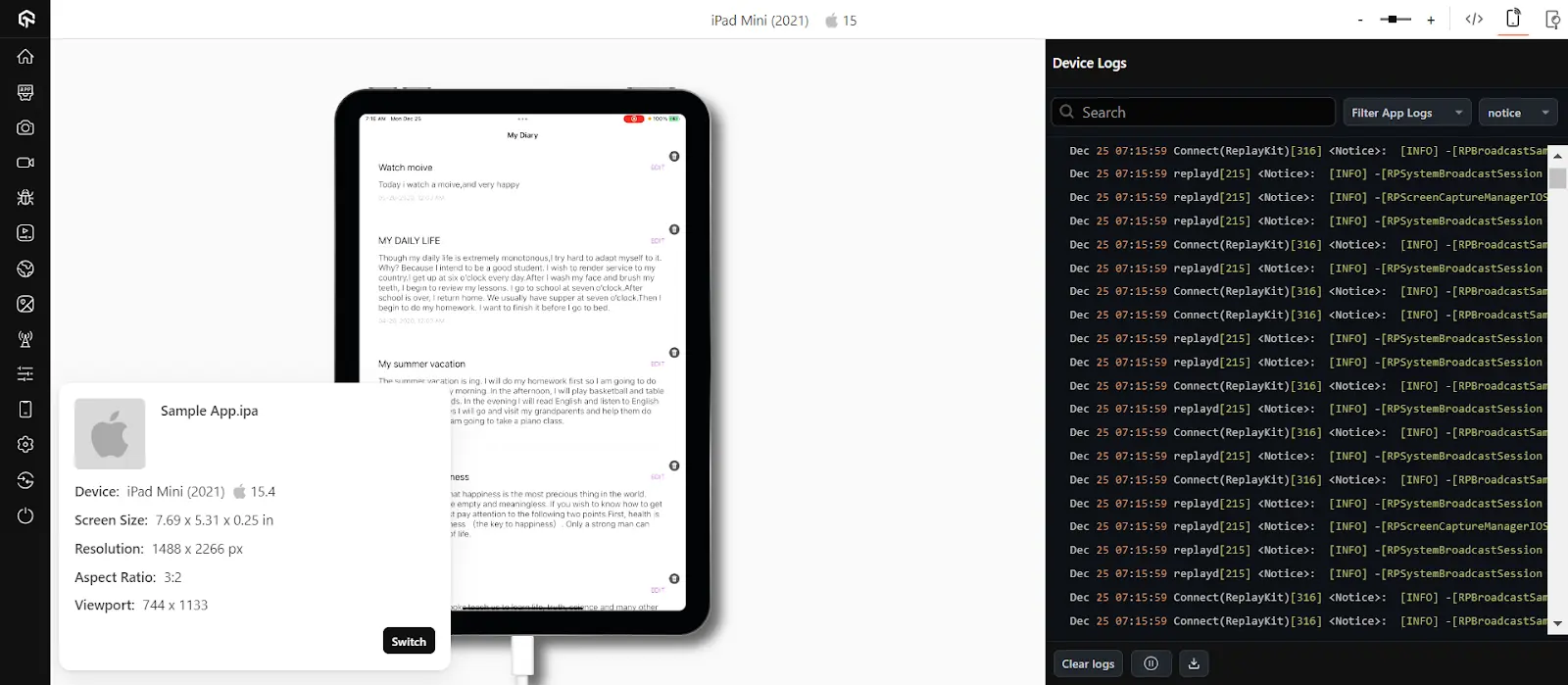
For more information, check out the tutorial below on how to perform real-time testing on LambdaTest.
In addition, LambdaTest also allows you to perform automation testing at scale. In case you plan to move from manual to automation testing, you can give LambdaTest a spin.
So, in this section, we looked at performing manual testing on the cloud-based grid and reaping additional benefits these platforms offer. However, there are also some myths associated with manual testing.
Common Myths of Manual Testing
Let’s discuss some of the myths associated with the manual test process.
- Myth 1: Testing is easy One common misconception in the testing world is that manual testing is easy. It's a natural tendency for people to label things as easy when they have some knowledge about them. However, the truth is, we often find things difficult when we lack knowledge about them.
- Myth 2: Anyone can do testing Building on the first myth, there's a belief that anyone can do testing. This is not the case. Testing requires passion. While it may sound appealing at first, real testing involves thinking outside the box and attempting to break systems. It takes something special to be a tester.
- Myth 3: Manual testing is obsolete A prevalent myth is that manual testing is obsolete and automation has taken its place. This is not true. Manual testing is the backbone of the testing phase, and automation comes after the product has achieved stability. Manual testing ensures a stable product is delivered to customers, and automation enhances that stability for end users.
- Myth 4: Manual testers have low pay Due to the aforementioned myths, some believe that manual testers receive low pay. In certain organizations, especially those run by non-technical individuals, manual testers may be undervalued. However, well-established organizations, led by professional technical experts, recognize the importance of experienced manual testers and offer compensation that aligns with their skills and contributions. In case you are planning to kick start your career in manual testing, prepare yourself with these manual testing interview questions and answers.
- Myth 5: Testers have weak coding skills Another common misconception is that testers have weak coding skills. In reality, testing often involves coding. Testers create complex SQL queries for data validation, modify code for database migration testing, and write scripts in languages like Java or Python for automation testing. Testing requires a strong understanding of coding principles.
Testing software manually is a crucial part of the software development journey, allowing testers to replicate real-world user experiences and pinpoint flaws in software products. Despite its importance, manual testing presents testers with a set of challenges that they must navigate to uphold product quality.
Challenges with Manual Testing
With software releases becoming a common thing, it's imperative that the testing process initiates early, right from the requirements specification and planning phase. However, manual testing encounters several challenges that need to be addressed before streamlining the testing cycle.
- Repetitive Testing Tasks: Manual testers often grapple with the repetitiveness of their tasks, particularly in regression testing where the same test cases are executed repeatedly. At times, this can result in oversight due to a lack of engagement.
- Test Data Management: Handling test data becomes a formidable challenge, especially with large and complex software applications. Testers must ensure that test data remains accurate, consistent, and relevant to various test scenarios. The manual creation and maintaining of test data sets can be both time-consuming and error-prone.
- Test Environment Setup: Creating test environments that mimic the production environment can pose challenges. Discrepancies between the test and production environments may yield false positives or negatives in testing results.
- Test Case Documentation: The creation and maintenance of comprehensive test cases are pivotal for effective manual testing. Testers need to keep up-to-date test cases, cover all relevant scenarios, and ensure they are easily understandable by the testing team.
- Time Constraints: Balancing project deadlines with thorough testing can be stressful. Testers frequently face time constraints that may result in insufficient test coverage thereby impacting the software quality.
- Communication and Collaboration: Successful testing relies on effective communication with developers, product managers, and other team members. Miscommunication or a lack of collaboration can lead to misunderstandings, incorrect expectations, and complications in defect resolution.
- Adaptation to Frequent Changes: In agile development environments, product requirements and features undergo rapid changes. Testers must be adaptable and prepared to modify test cases and plans at short notice to accommodate these changes.
- Test Data Privacy and Security: Protecting sensitive test data poses a significant concern, especially for applications handling personal or financial information. Testers must ensure data privacy and security while testing the product, a task that can be challenging in some instances.
- Browser and Device Fragmentation: Testing across various devices, operating systems, and browsers for cross-compatibility can be a substantial challenge. each combination may necessitate separate testing, escalating the workload for manual testers.
- Test Reporting and Documentation: Generating and maintaining test reports and documentation takes considerable amount of time. Clear and well-documented reports are crucial for tracking defects and ensuring all stakeholders have a clear understanding of the testing progress and results.
To ensure a good web and mobile experience, detailed software testing is crucial. However, it can become complex and costly if not properly planned. Therefore, software teams need to approach manual testing in a systematic and planned manner.
Manual Testing Best Practices
Testers should follow some of the best practices while performing manual testing.
- Thoroughly understand the project's specifications and create documents before starting the testing process. It ensures that your testing is aligned with the intended functionality.
- Clearly outline the scope of testing, along with specific objectives and a defined approach, helps set expectations and provides a roadmap for the testing process.
- Integrate risk analysis into the testing process. Understanding the business impact of potential defects and focusing on critical functionalities ensures that testing efforts are prioritized effectively.
- Follow an incremental testing approach and break down the testing process into different components. This can enhance efficiency, allow for early defect detection, and make it easier to track progress.
- Create test cases that are easy to understand, scalable for future changes, and concise for efficient execution and maintenance. Also, write test cases with reusability in mind contributes to efficiency and consistency across different testing phases and iterations.
- Exploratory and ad hoc testing can identify unexpected defects and help ensure thorough test coverage.
- Effective communication with the development team, stakeholders, and other project members fosters collaboration, helps address issues quickly, and ensures everyone is on the same page.
- Perform UI testing to identify issues related to layout, design, responsiveness, and usability, which can significantly impact user satisfaction.
- Stay informed about the product and testing methodologies contributes to professional development and improved testing practices.
Conclusion
In this manual testing tutorial, we discussed the characteristics of manual testing, its pros and cons, core techniques, types of manual testing, and how to perform manual testing by leveraging the potential of cloud testing platforms.
Testing software manually requires a tester to have patient, creative, and open-minded. It's a crucial aspect of creating user-friendly software because, ultimately, people are using these applications and testers must approach their work with the mindset of an end user. Thinking from the end user's perspective is key to ensuring the software meets their needs effectively.
- Overview
- What is Manual Testing?
- Why is Manual Testing Important?
- Characteristics
- Advantages and Shortcomings
- Manual Testing vs Automation Testing
- Core Techniques
- Types
- Manual Testing Process
- Example
- How to Perform on Cloud
- Common Myths
- Challenges
- Manual Testing Best Practices
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)





 A cloud-based operating system will be launched where you can manually test your websites and web applications.
A cloud-based operating system will be launched where you can manually test your websites and web applications. 
 For demonstration purposes, let’s choose Real Device.
For demonstration purposes, let’s choose Real Device. It will route you to the selected cloud-based device.
It will route you to the selected cloud-based device. 